Author: Azhar Amir - professional writer who has worked for organizations such as UNDP, FAO, UNODC, and UNICEF
Evolution of the agricultural industry & its importance
Agriculture is an important aspect of human civilization and is the foundation of modern society. Agriculture deep connections to the world economy, biodiversity, and human lives and history cannot be refuted. It is the world’s largest industry, employing over 1.3 billion people (ILO, n.d.) and valued at $5 trillion (Goedde, 2015). Agriculture enabled us to grow our own food, as a result, human effectively evolved from being a hunting society to self-sustain one.
Competition of scarce resources & role of agribusiness companies
Agricultural value chain encompasses wide range of activities ranging from farmer (agricultural machinery, seeds, fertiliser, pesticides) to consumer.
Agriculture sector broadly can be divided at three main levels i.e. production, industrial processing and retail or wholesale distribution. Each stage is link with other and add value either in the form of services inputs or goods. Agriculture is heavily depend on scarce resources like water, arable land and biodiversity. At each level of supply chain different players perform different functions e.g. producers, consumers and organisations who provide factor of production such as seeds, fertiliser and pesticides.
With increasing population and traditional means of agriculture, natural resources such as water is depleting at fast rate. Agriculture is largest consumer of the Earth available freshwater almost 70 percent (WWF, 2015).
Graph of global agricultural water withdrawal

Source: http://www.globalagriculture.org/report-topics/water.html
Some of crops e.g. sugarcane and cotton are most water intensive crops. Therefore, finding new ways to use water resourcefully in agriculture sector is very critical.
Agribusiness companies are playing very important role and are already looking for ways to produce seeds and fertiliser that require less water. Increasing agricultural yield and investing in agricultural are vital for world food security in a world in which one in seven people goes hungry.
According to Goedde, Horii and Sanghvi (2015) satisfying world food wants also opens new door for agribusiness companies to invest throughout the value chain. Therefore role of factor providers with in agriculture sector is of paramount importance.
In last five decades, agriculture productivity has increased as a result of new technology and innovation made by agribusiness companies, which have enabled farmers to produce plentiful food in many parts of the world. However, with rapidly increasing population, feeding global population has resurfaced as a critical problem. According to World Bank (2015) report, if current trend continues by 2050 we have to feed 9 billion people and agriculture system need to produces about 50 percent more food.
Graph of world population 1950–2050
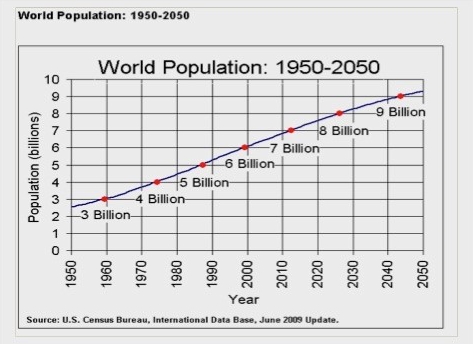
Source: https://www.census.gov/population/international/data/idb/worldpopgraph…
In order to meet this daunting challenge global food production needs to be increase on large scale. In the past Agribusiness sector responded to this challenge through innovation in the field of agriculture by introducing new technology and high yield seed varieties.
Agriculture industry & innovation
The industrial agriculture sector is no stranger to innovation phenomenon. About 10,000 years ago, early humans’ harvested food from natural surroundings, and in the process, learnt to domesticate crops and animals. Eventually, they began to select better plant materials for propagation and animals for breeding with the intention of developing improved food crops and livestock (Wieczorek, 2012). Over the centuries, agriculture technologies have evolved from simple equipment to complex machinery, chemistry, seed and information management (Graff, 2003).
Many of us are surprised to know genetically modified seed (GM) is not new. Human have been doing this for thousands of years e.g. at beginning of domestic agriculture through selective breeding farmers changed makeup of crops they grew and livestock they raised. Nearly every grain and vegetable available today has been altered by human hands (BiotechNow, 2015).
A timeline of innovation in biotechnology
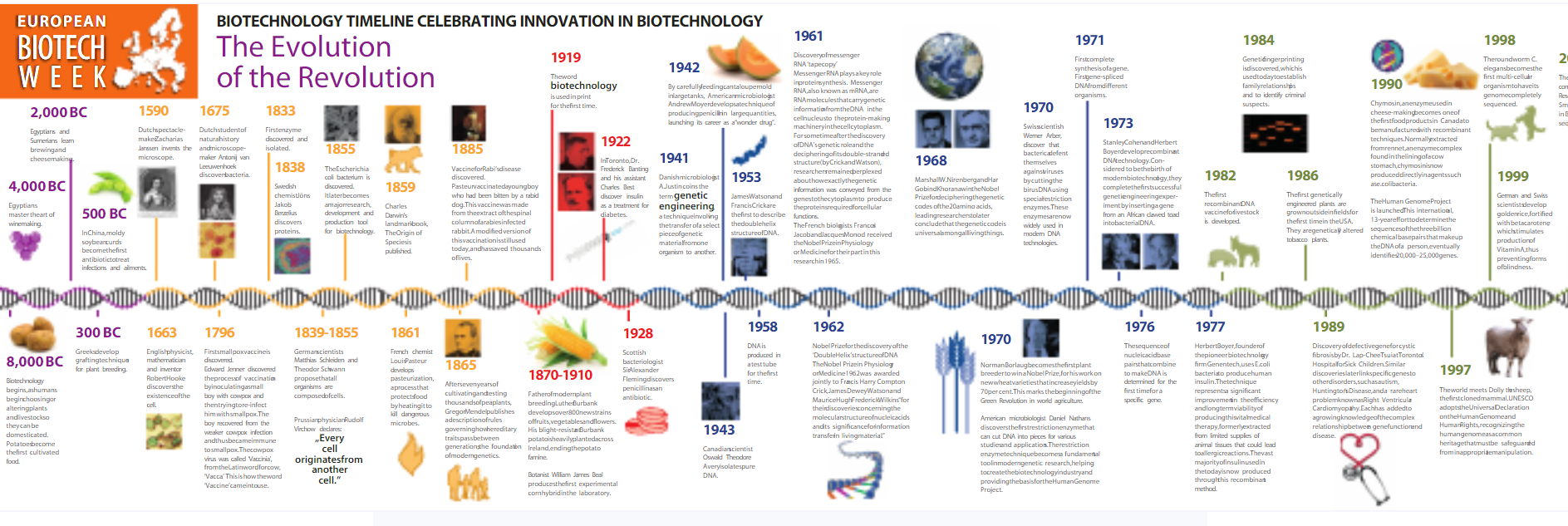
Source: biotech-now.org
Over the last 30 years and continuing through to the present, agribusiness companies have responded to this challenge through R&D innovations. These innovations largely span four fields – Genetic Traits and Seeds (Phillips McDougall, 2011), Agrochemicals (Phillips McDougall, 2014), Agricultural Biologicals (Kroll, 2013), and Precision Agriculture (Clancy, 2014).
Innovation in agriculture took a new turn in the early 1980s when several chemical firms started researching into a new field called biotechnology. Genetic modification (GM) technologies (heavily dependent on patents) revolutionised the genetic and agrichemical inputs sectors and it is at the epicenter of the innovation efforts in modern agriculture. GM technology benefited across the food chain and environment. It has helped to produced sustainable food, increased productivity, increased use of conservation tillage and biodiversity, reduction in the use of pesticides.
Therefore, in the face of increased micro- and macro-economic challenges, the imperative for agribusinesses to continue innovating assumes even more importance.
References
- Wilkinson, J. (2009). The Globalization of Agribusiness and Developing World Food Systems. An Independent Specialist Magazine, monthly review., 61(04), 20-51. Retrieved Jan 2, 2020.
- Boccaletti, G., Grobbel, M., & Stuchtey, M.R. (2009, December). The business opportunity in water conservation. Retrieved Dec 20, 2020, from McKinsey Quarterly: http://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/sustainability-and-resource-….
- Goedde, L., Horii, M., & Sanghvi, S. (2015). Pursuing the global opportunity in food and agribusiness. Retrieved Dec 25, 2020 from Mckinsey Quarterly. http://www.mckinsey.com/industries/chemicals/our-insights/pursuing-the-….
- World Bank (2014, March 31). Land and Food Security. Retrieved Dec 25, 2020, from http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/agriculture/brief/land-and-food-secur…
- Arjylee, S. C. (2015 July 10).Giant Companies in the Agriculture Industry. Retrieved Dec 26, 2020, from http://foundersguide.com/top-agricultural-companies-in-the-world/
- FAO (2015). Food and Agriculture in National and International Settings. Retrieved Dec 26, 2020, from http://www.fao.org/docrep/004/y3557e/y3557e07.htm
- Sherrard, J. (2015, January 15). To feed the world, food and agriculture industry must embrace innovation. Retrieved Dec 10, 2020, from http://www.theguardian.com/sustainable-business/2015/jan/15/feed-world-….
- Castro, S. A. (2015, July 15). Giant Companies in the Agriculture Industry. Retrieved Dec 20, 2020, from http://foundersguide.com/top-agricultural-companies-in-the-world.
- World Bank (2014). Agriculture Sector Results Profile. Retrieved Dec 20, 2020, from http://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2013/04/15/agriculture-results-prof…
- BIOtechNOW (2015).Get to Know GMOs Month Launches Today. Retrieved Dec 10, 2020, from http://www.biotech-now.org/food-and-agriculture/2015/10/get-to-know-gmo….
- Lianos, I., Katalevsky, D., & Ivanov, A. (2016). The Global Seed Market, Competition Law and Intellectual Property Rights: Untying the Gordian knot. Centre for Law, Economics and Society Research Paper Series.